- writer_xyz 的博客
Sleeping Cup #5 Editorials
- @ 2025-7-27 23:50:00
A - 汽水
注意到每次加一吨原料后搅拌多于一次都是没有意义的:
- 如果第二次的搅拌深度与第一次相同,那么第二次搅拌显然没有意义。
- 如果第二次的搅拌深度小于第一次,那么第二次搅拌实际上就是在将已经混匀的原料混匀,因此第二次搅拌没有意义。
- 如果第二次的搅拌深度小于第一次,那么第一次搅拌所涉及的那一部分原料是否经过第一次搅拌其实不影响第二次搅拌的效果,于是第一次搅拌没有意义。
也就是说,我们只需要枚举每次加的原料和每次加原料后搅拌的深度(也可能不搅拌),直接上 的迭代加深搜索即可,搜索到 就能搜索出正确答案。
7 10
1 0 2 1 1 1 1 5 0 5
972f2cb1b8c6a87de4649570fbad2c68
B - 平方差
众所周知:
- 。
- 。
- 。
- 对于 无解。
- 以上式子中 为非负整数。
直接分情况讨论即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
freopen("sd.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("sd.out", "w", stdout);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
long long n;
cin >> n;
if (!n)
{
cout << "0 0" << endl;
continue;
}
switch (n % 4)
{
case 0:
{
cout << n / 4 + 1 << ' ' << n / 4 - 1 << endl;
break;
}
case 2:
{
cout << "-1 -1" << endl;
break;
}
default:
{
cout << n / 2 + 1 << ' ' << n / 2 << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
C - 比赛
在合法的排名表中,不难发现以下性质:
- 如果 A 的成绩比 B 高,那么 B 的成绩比 A 低。
- 如果 C 的成绩比所有人都高,那么他(她)是第一名。
- 在上面一条的基础上,每出现一个比 C 成绩高的选手,C 的排名就增加一名。
根据以上性质确定所有人的排名后一一代入验证即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000 + 12;
char c[N][N];
int rk[N];
int sta[N];
int main()
{
freopen("match.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("match.out", "w", stdout);
int T;
scanf("%d ", &T);
while (T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d ", &n);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= i - 1; j++)
{
scanf("%c ", &c[i][j]);
c[j][i] = '>' + '<' - c[i][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
rk[i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (i != j && c[i][j] == '<') rk[i]++;
}
bool ok = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (i == j) continue;
if (rk[i] <= rk[j] && c[i][j] == '<') ok = false;
if (rk[i] >= rk[j] && c[i][j] == '>') ok = false;
}
if (!ok)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
printf("-1 ");
puts("-1");
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
sta[rk[i]] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
printf("%d ", sta[i]);
printf("%d\n", sta[n]);
}
}
return 0;
}
D - 二元运算
设取模前的答案为 。
打表可知,当 时,。
根据以上性质,我们直接对 的情况按照 暴力计算即可。
(实际上,这一性质是可以严格证明的,过程如下:)
$$\begin{aligned} x \otimes 119 &=\dfrac{119^2+2023x}{833+119x} \\ &=\dfrac{14161+2023x}{833+119x} \\ &=\dfrac{2023(7+x)}{119(7+x)} \\ &=\dfrac{2023}{119} \\ &=17 \end{aligned} $$$$\begin{aligned} f(n) &=n \otimes (n-1) \otimes (n-2) \otimes \ldots \otimes 1 \\ &=((n \otimes (n-1) \otimes (n-2) \otimes \ldots \otimes 120) \otimes 119) \otimes 118 \otimes 117 \otimes \ldots \otimes 1 \\ &=17 \otimes 118 \otimes 117 \otimes \ldots \otimes 1 \\ &\equiv 40176944 \pmod {10^8+7} \end{aligned} $$#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int P = 1e8 + 7;
int read()
{
int x = 0;
char c = getchar_unlocked();
while (c < '0') c = getchar_unlocked();
while (c >= '0')
{
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
c = getchar_unlocked();
x = min(x, 1000);
}
return x;
}
int divs(int a, int b, int p = P)
{
if (b % a == 0) return b / a;
int x = divs(p % a, a - b % a, a);
return (1ll * x * p + b) / a;
}
long long calc(long long x, long long y)
{
return divs((833 + x * y) % P, (y * y + 2023 * x) % P);
}
signed main()
{
freopen("calc.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("calc.out", "w", stdout);
int T = read();
while (T--)
{
int n = read();
int res = n;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
res = calc(res, i);
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
E - 评测记录
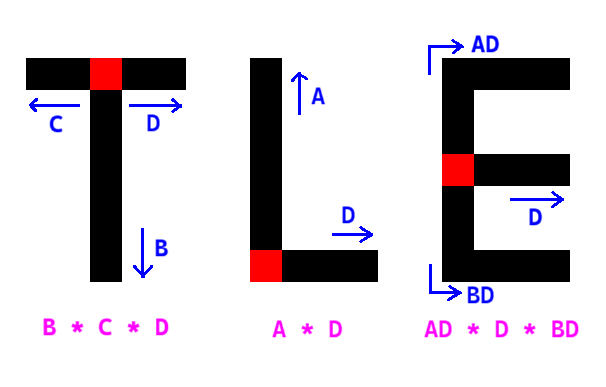
求出上图中需要的数组后,按照上图给出的计数方式枚举红色枢纽点统计即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000 + 12, P = 1e4 + 7;
int X[N][N][7];
// 0 - 6: input, A, B, C, D, A + D, B + D
int main()
{
freopen("record.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("record.out", "w", stdout);
signed n, m;
__int128 T = 0, L = 0, E = 0;
scanf("%d %d ", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
char c;
scanf("%c ", &c);
if (c == 'G') X[i][j][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][1] = X[i - 1][j][1] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
X[i][j][1] = max(X[i][j][1] - 1, 0);
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][2] = X[i + 1][j][2] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
X[i][j][2] = max(X[i][j][2] - 1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][3] = X[i][j - 1][3] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
X[i][j][3] = max(X[i][j][3] - 1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = m; j >= 1; j--)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][4] = X[i][j + 1][4] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
X[i][j][4] = max(X[i][j][4] - 1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][5] = X[i - 1][j][5] + X[i - 1][j][4];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][5] -= X[i - 1][j][4];
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][6] = X[i + 1][j][6] + X[i + 1][j][4];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (X[i][j][0]) X[i][j][6] -= X[i + 1][j][4];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
T += (__int128) X[i][j][2] * X[i][j][3] * X[i][j][4];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
L += (__int128) X[i][j][1] * X[i][j][4];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
E += (__int128) X[i][j][4] * X[i][j][5] * X[i][j][6];
T %= P, L %= P, E %= P;
cout << (int) T << ' ' << (int) L << ' ' << (int) E << endl;
return 0;
}
F - 逆序对
用线段树或分块对每个区间维护以下信息即可:
- 区间反转的 lazytag;
- 区间内 的个数。
- 区间内逆序对的个数。
当反转区间 时,设其长度为 ,后两个标记的值分别为 :
- 。
- $y' \gets \dfrac{1}{2}s(s-1)-\dfrac{1}{2}x(x-1)-\dfrac{1}{2}(s-x)(s-x-1)-y$。
- 为总二元组个数。
- 为反转前的 二元组个数,反转后变为 。
- 为反转前的 二元组个数,反转后变为 。
- 为反转前的 二元组个数,反转后变为 。
- 从总数中减去上面三种不合法情况后,剩下的 就是合法情况。它表示反转前 二元组个数,反转后变为 。
当合并区间 至区间 时( 在前面),设其长度为 ,后两个标记的值分别为 :
- 。
- 。
- 为 中的逆序对个数。
- 为 中的逆序对个数。
- 为跨越 的逆序对个数,它一定由 中的一个 和 中的一个 组成,因此其数量等于 中 的个数乘上 中 的个数。
- 这三种情况加起来,就是总的逆序对个数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int unsigned
using namespace std;
const int N = 1 << 16, M = 1 << 18, I = (int) INT_MAX + 1;
int sum[M], invc[M];
bool rev[M];
inline int read()
{
int x = 0;
char c = getchar_unlocked();
while (c < '0') c = getchar_unlocked();
while (c >= '0') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar_unlocked();
return x;
}
inline void write(int x)
{
if (!x) return;
write(x / 10);
putchar_unlocked(x % 10 + '0');
}
inline void writeline(int x)
{
if (x) write(x);
else putchar_unlocked('0');
putchar_unlocked('\n');
}
inline int pairs(int x)
{
return x * (x - 1) >> 1;
}
inline bool update(int pos, int ssz, int all)
{
rev[pos] = !rev[pos];
invc[pos] = all - invc[pos];
invc[pos] -= pairs(sum[pos]);
sum[pos] = ssz - sum[pos];
invc[pos] -= pairs(sum[pos]);
return rev[0];
}
inline bool pushdown(int pos, int spos, int ssz, int all)
{
rev[pos] = !rev[pos];
return update(spos, ssz, all) | update(spos | 1, ssz, all);
}
inline bool pushup(int pos, int spos, int ssz)
{
sum[pos] = sum[spos] + sum[spos | 1];
invc[pos] = invc[spos] + invc[spos | 1] + sum[spos] * (ssz - sum[spos | 1]);
return rev[0];
}
bool reverse(int l, int r, int nl, int nr, int sz, int pos)
{
if (l == nl && r == nr) return update(pos, sz, pairs(sz));
int lm = (nl + nr) >> 1, rm = lm + 1, ssz = sz >> 1, spos = pos << 1;
if (rev[pos]) pushdown(pos, spos, ssz, pairs(ssz));
if (l <= lm) reverse(l, min(lm, r), nl, lm, ssz, spos);
if (r >= rm) reverse(max(rm, l), r, rm, nr, ssz, spos | 1);
return pushup(pos, spos, ssz);
}
pair <int, int> count(int l, int r, int nl, int nr, int sz, int pos)
{
if (l == nl && r == nr) return make_pair(sum[pos], invc[pos]);
int lm = (nl + nr) >> 1, rm = lm + 1, ssz = sz >> 1, spos = pos << 1;
pair <int, int> al = make_pair(I, 0), ar = make_pair(I, 0);
if (rev[pos]) pushdown(pos, spos, ssz, pairs(ssz));
if (l <= lm) al = count(l, min(lm, r), nl, lm, ssz, spos);
if (r >= rm) ar = count(max(rm, l), r, rm, nr, ssz, spos | 1);
int res1 = al.first + ar.first, res2 = max(al.second, ar.second);
if (res1 < I) res2 = al.second + ar.second + al.first * (r - lm - ar.first);
return make_pair(res1 & INT_MAX, res2 | pushup(pos, spos, ssz));
}
signed main()
{
freopen("inversion.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("inversion.out", "w", stdout);
int n = read(), q = read() << 1;
while (q--)
{
int l = read(), r = read();
if (q & 1) reverse(l, r, 0, N - 1, N, 1);
else writeline(count(l, r, 0, N - 1, N, 1).second);
}
return 0;
}
G - 遗失的平面
让我们先约定一些记号:
- 和 代指要复原的两个平行平面。
- 和 分别代指 和 上的点。
- 代指直线 ,即通过点 和点 的直线。
- 代表点 在直线 上。特别地, 代表 三点共线。
- 代表点 不在直线 上。特别地, 代表 三点不共线。
- 代表点 在平面 上。
- 代表直线 在平面 上。
- 代指 和 的法向量。
- 代指 的法向量,其求法请参考 Luogu P4894。
- 代指 所在的平面。
- 代表向量 和 共线。
- 代表向量 和 不共线。
- 代表对应元素平行,其中 为直线, 为平面。
- 代表对应元素垂直,其中 为直线, 为平面。
- 代指 和 所在的平面平行,这等价于 。
在回到正题之前,让我们考虑三个特殊情况——
特殊情况 :,此时输出 01 显然正确。
实际上, 时一定有解——过点 作平面 ,过点 作平面 ,就可以得到满足要求的一组平面 和 ,其中 和 是给出的两个点, 代指直线 。
特殊情况 :,此时可以直接枚举划分方案。设所划分的 组(每组 个)点分别是 ()和 (),并用 代指直线 , 代指直线 。由立体几何基本事实 2(或者此处的公理 1)的推论——直线与平面相交有且只有一个公共点,可知 。实际上,这个划分方案合法,当且仅当 和 平行或异面。
当 和 平行时,由立体几何基本事实推论 3,同时满足 和 的平面 有且只有一个。过直线 作平面 ,过直线 作平面 ,就可以得到满足要求的一组平面 和 。
当 和 异面时,过点 作直线 ,过点 作直线 ,那么同时满足 、、、、、、、 的平面 都是唯一确定的。根据线面平行的判定定理和面面平行的判定定理,由 可知 ,由 可知 ,从而 ——我们得到了满足要求的一组平面 和 。
当 和 相交时,设 和 的交点是 ,那么由 和 ,可知 ——这与 矛盾。也就是说, 和 相交时,不存在满足要求的平面 和 。
特殊情况 :如果数据中存在 点共线(即存在 满足 ,其中 ),那么在所有合法的构造中,这 个点一定落在同一个点。
让我们考虑使用反证法证明上述断言的正确性——让我们先假设上述断言是不正确的。
因为数据保证有解,所以一定存在另外一组平行但不重合的平面 和 ,使得:
- 每个给定的点(包括 )都恰好落在 和 中的某一个平面上。
- 和 都包含了 中的至少一个点。
因为直线与平面相交有且只有一个公共点,结合上面的性质,可知 和 都包含了 中的恰好一个点。
根据上述论证,结合上述断言所需要的前提条件,我们得到了以下结论:
- 每个给定的点(包括 )都恰好落在 和 中的某一个平面上。
- 和 一共包含了 中的 个点。
- 。
这 条结论显然矛盾,因此假设不成立,上述断言一定是正确的。
接下来,我们回到正题。在下面的叙述中,我们默认 ,因为 的情况已经在上面讨论过了。
不难看出,任取 个点(比如 )就一定会有 个点同时落在 (或 )上,因此我们只需要尝试 次就能确定 个落在同一个待复原平面上的点。
不妨设 均在 上,那么有:
- 由立体几何基本事实 2,如果 ,那么一定有 。
- 对于满足 的 ,。
- 对于 ,。
这启示我们(当 时)利用 map 对每个不同方向的 统计出现次数——一定有恰好 个给定的点 满足 。
因此,我们只需要对每个出现次数符合要求的(可能的),判定剩下 个满足 的点 是否在同一个法向量也为 的平面上(如果判定成功,那么这 个点所在的平面就是平面 )就可以了——这可以通过(先任取 中的 个点——不妨设这 个点分别是 和 ,然后)对 检查其是否满足 和 中的至少一条来实现。如果判定成功,我们直接对 输出 0,对另外 个点输出 1,即可完成构造。
然而,如果数据中存在 点共线(即存在 满足 )的情况,那么我们在最坏情况下就需要判定 次,上述做法的时间复杂度将退化为 (其中 是 map 贡献的, 是化简法向量时使用的 __gcd 贡献的,且最坏情况下 ),无法通过此题。
让我们考虑对每个 的判定进行优化。观察发现,我们可以另取 个点 (,),并(当 时)利用(另一个)map 对每个不同方向的 统计出现次数。对于每个 :
- 若 或 (注意到这样的 最多只有 个,因为 和 各自只能对应一个方向的 ),依然按原来的方法判断。
- 若 且 ,那么 中一定包含了 ,我们只需要判定另外 个 是否满足 即可。此时我们的另一个
map就派上用场了——因为对于 一定有 (否则由 得 ,然而 和 有公共点 ,矛盾),所以我们只需要判定(当 时)是否有恰好 个给定的点 满足 即可。
应用这一优化后,上述做法的时间复杂度将下降至 ,可以通过本题。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e4 + 12;
struct P
{
int x, y, z;
};
const P E = (P){0, 0, 0};
P operator-(P x, P y)
{
return (P){x.x - y.x, x.y - y.y, x.z - y.z};
}
bool operator==(P x, P y)
{
__int128 rt1 = 0, rt2 = 0;
if (x.x == 0 && y.x != 0) return false;
if (x.x != 0 && y.x == 0) return false;
if (x.y == 0 && y.y != 0) return false;
if (x.y != 0 && y.y == 0) return false;
if (x.z == 0 && y.z != 0) return false;
if (x.z != 0 && y.z == 0) return false;
if (x.x != 0) rt1 = x.x, rt2 = y.x;
if (x.y != 0) rt1 = x.y, rt2 = y.y;
if (x.z != 0) rt1 = x.z, rt2 = y.z;
if (x.x * rt2 != y.x * rt1) return false;
if (x.y * rt2 != y.y * rt1) return false;
if (x.z * rt2 != y.z * rt1) return false;
return true;
}
bool operator!=(P x, P y)
{
return !(x == y);
}
bool straight(P x, P y)
{
return (__int128) x.x * y.x + (__int128) x.y * y.y + (__int128) x.z * y.z == 0;
}
P simplify(P a)
{
int d = max(abs(a.x), max(abs(a.y), abs(a.z)));
if (a.x) d = __gcd(abs(a.x), d);
if (a.y) d = __gcd(abs(a.y), d);
if (a.z) d = __gcd(abs(a.z), d);
if (a.x < 0) d = -d;
if (a.x == 0 && a.y < 0) d = -d;
if (a.x == 0 && a.y == 0 && a.z < 0) d = -d;
if (d) a.x /= d, a.y /= d, a.z /= d;
return a;
}
P in[N];
bool ans[N];
P normal(int x, int y, int z)
{
P a = in[x] - in[y], b = in[x] - in[z];
int nx = a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y;
int ny = a.z * b.x - a.x * b.z;
int nz = a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
return (P){nx, ny, nz};
}
bool operator<(P x, P y)
{
if (x.x != y.x) return x.x < y.x;
if (x.y != y.y) return x.y < y.y;
return x.z < y.z;
}
bool check(int x, int y, int n)
{
if (n == 2)
{
P p1 = in[x], p2 = in[y], p3 = in[6 - x - y], p4 = in[4];
if (p1 - p2 == p1 - p3 || p1 - p2 == p1 - p4) return false;
if (p1 - p2 == p3 - p4 || normal(x, y, 6 - x - y) != normal(x, y, 4))
{
ans[x] = ans[y] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
printf("%d", ans[i]);
puts("");
return true;
}
return false;
}
memset(ans, 0, sizeof ans);
ans[x] = ans[y] = true;
map<P, int> mp1, mp2;
int line = 2;
P curline = in[x] - in[y];
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
if (i == x || i == y) continue;
if (in[x] - in[i] == curline)
{
line++;
ans[i] = true;
continue;
}
P cur = simplify(normal(x, y, i));
if (!mp1.count(cur)) mp1[cur] = 1;
else mp1[cur]++;
}
if (line == n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
printf("%d", ans[i]);
puts("");
return true;
}
int xx = 1;
while (x == xx || y == xx || ans[xx]) xx++;
int yy = xx + 1;
while (x == yy || y == yy || ans[yy]) yy++;
int lines = 2;
P curlines = in[xx] - in[yy];
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
if (i == x || i == y || i == xx || i == yy) continue;
if (in[xx] - in[i] == curlines)
{
lines++;
continue;
}
P cur = simplify(normal(xx, yy, i));
if (!mp2.count(cur)) mp2[cur] = 1;
else mp2[cur]++;
}
if (lines == n)
{
memset(ans, 0, sizeof ans);
ans[xx] = ans[yy] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
if (i == xx || i == yy) continue;
if (in[xx] - in[i] == curlines)
{
ans[i] = true;
continue;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
printf("%d", ans[i]);
puts("");
return true;
}
for (map<P, int>:: iterator s = mp1.begin(); s != mp1.end(); s++)
{
if ((s -> second) != n - line) continue;
P now = (s -> first);
if (normal(x, y, xx) != now && normal(x, y, yy) != now)
{
if (!mp2.count(now)) continue;
if (mp2[now] != n - lines) continue;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
if (i == x || i == y || i == xx || i == yy) continue;
if (ans[i]) continue;
if (in[xx] - in[i] == curlines) continue;
P cur = normal(x, y, i);
if (cur == now) ans[i] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
printf("%d", ans[i]);
puts("");
return true;
}
else
{
int xxx = 1;
while (x == xxx || y == xxx || normal(x, y, xxx) == now || ans[xxx]) xxx++;
int yyy = xxx + 1;
while (x == yyy || y == yyy || normal(x, y, yyy) == now || ans[yyy]) yyy++;
bool oks = true;
P nows = in[xxx] - in[yyy];
if (!straight(nows, now)) oks = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
if (i == x || i == y || i == xxx || i == yyy) continue;
if (ans[i]) continue;
if (in[xxx] - in[i] == nows) continue;
if (normal(x, y, i) == now) continue;
P cur = normal(xxx, yyy, i);
if (cur != now) oks = false;
}
if (!oks) continue;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
if (i == x || i == y || i == xxx || i == yyy) continue;
if (ans[i]) continue;
if (in[xxx] - in[i] == nows) continue;
P cur = normal(x, y, i);
if (cur == now) ans[i] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
printf("%d", ans[i]);
puts("");
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int solve()
{
memset(ans, 0, sizeof ans);
signed n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
{
signed x, y, z;
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &z);
in[i] = (P){x, y, z};
}
if (n == 1)
{
puts("01");
return 0;
}
if (check(1, 2, n)) return 0;
if (check(1, 3, n)) return 0;
if (check(2, 3, n)) return 0;
// The two statements below will be never executed.
puts("I hate computational geometry!!!");
return 0;
}
signed main()
{
freopen("surface.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("surface.out", "w", stdout);
signed T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
